Content

Therefore, the amount of bad debt expenses a company reports will ultimately change how much taxes they pay during a given fiscal period. In order to comply with the matching principle, bad debt expense must be estimated using the allowance method in the same period in which the sale occurs. If a company has significant risk of uncollectible accounts or other problems with receivables, it is required to discuss this possibility in the notes to the financial statements. Uncollectible accounts receivable are estimated and matched against sales in the same accounting period in which the sales occurred. Bad debt expenses related to the goods or services delivered to a customer. Since the initial items fall under the cost of goods sold, most people think it must include bad debts.
If you don’t have a lot of bad debts, you’ll probably write them off on a case-by-case basis, once it becomes clear that a customer can’t or won’t pay. A major concern when developing a bad debt expense is when new products are being sold, since there is no historical information on which the expense estimate can be based. In this case, one option is to base the expense on the most similar product for which the organization has historical data.
It is not accurate for the business to only record accounts receivable as a short-term asset because not all of these outstanding debts will be paid. The bad debt expense calculation under the allowance method can be determined in a number of ways.
The main purpose of bad debt expense recording is to ensure that your financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP—Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. The concept of bad debt expense should be well familiar to business-to-business sellers and other merchants who invoice their customers under Net 30 or similar terms. Sometimes clients go out of business, staff turnover leads to disorganization, or disputes blow up, and an invoice never gets paid. For retail merchants who charge up front for the goods they sell, unpaid receivables aren’t quite so relevant to their day-to-day bookkeeping.

At some point in time, almost every company will deal with a customer who is unable to pay, and they will need to record a bad debt expense. A significant amount of bad debt expenses can change the way potential investors and company executives view the health of a company. The original journal entry for the transaction would involve a debit to accounts receivable, and a credit to sales revenue. Once the company becomes aware that the customer will be unable to pay any of the $10,000, the change needs to be reflected in the financial statements. Two primary methods exist for estimating the dollar amount of accounts receivables not expected to be collected.
It should always be remembered that it is a very important accounting principle that assets must be correctly valued. In the above example, if a business knows that there is very little or no chance that the sum of $2137 will be paid, then there is a duty to re-adjust the value of the Accounts Receivable Asset. Bad Debts Expense is reported under “Selling expenses” in the income statement. Notes receivable are listed before accounts receivable because notes are more easily converted to cash. The notes receivable allowance account is Allowance for Doubtful accounts. Like accounts receivable, notes receivable can be readily sold to another party. Because of its emphasis on time, this schedule is often called an aging schedule, and the analysis of it is often called aging the accounts receivable.
The percentage of sales method simply takes the total sales for the period and multiplies that number by a percentage. Once again, the percentage is an estimate based on the company’s previous ability to collect receivables. The bad debt expense appears in a line item in the income statement, within the operating expenses section in the lower half of the statement. Because no significant period of time has passed since the sale, a company does not know which exact accounts receivable will be paid and which will default. So, an allowance for doubtful accounts is established based on an anticipated, estimated figure.
Unlock full control and visibility of disputes and provide better insight into how they impact KPIs, such as DSO and aged debt provisions. Harold Averkamp has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years. A common type of credit card is a national credit card such as Visa and MasterCard. The ratio Bad Debt Expense used to assess the liquidity of the receivables is the receivables turnover ratio. Pursue problem accounts with phone calls, letters, and legal action if necessary. Ask potential customers for references from banks and suppliers and check the references. If there is no hope of collection, the face value of the note should be written off.
The balance sheet aging of receivables method is more complicated than the other two methods, but it tends to produce more accurate results. It is important to consider other issues in the treatment of bad debts. This variance in treatment addresses taxpayers’ potential to manipulate when a bad debt is recognized. To remain consistent with the matching principle, businesses will write-off bad debt according to the allowance method. According to this method, the business will set aside a reserve for expected bad debts, or so-called doubtful accounts. This reserve, or allowance, is also referred to as a contra asset account because it “nets” or balances against the accounts receivable assets listed in the balance sheet. As an example of the allowance method, ABC International records $1,000,000 of credit sales in the most recent month.
Global and regional advisory and consulting firms bring deep finance domain expertise, process transformation leadership, and shared passion for customer value creation to our joint customers. Our consulting partners help guide large enterprise and midsize organizations undergoing digital transformation by maximizing and accelerating value from BlackLine’s solutions.
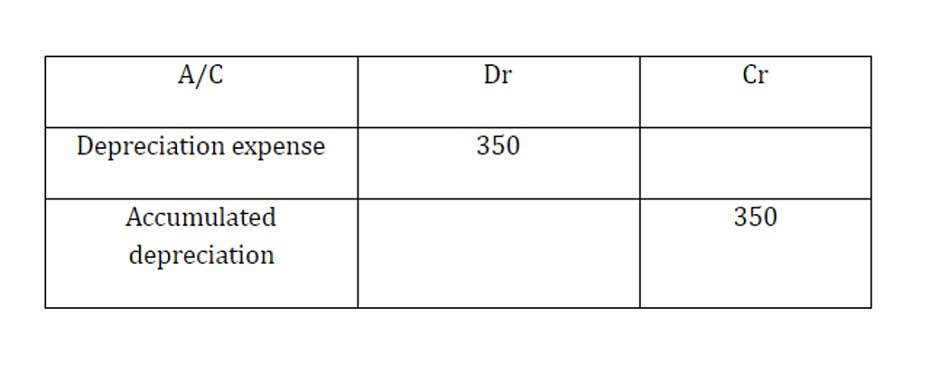
The accrual basis of accounting takes into consideration the income and expenses that are receivable or payable respectively for the financial year. Using the cash basis of accounting is no help since you have no income to set off the bad debt against. If this estimate is practical for future unpaid invoices, create an allowance for doubtful accounts at 10% of this year’s anticipated credit sales.
There is one option available for mortgages not available for the business debt – donation. The difference is that a valuation of $10,000 can be taken without an appraisal.
This method involves debiting your expense account and crediting the doubtful debts allowance with the same value here. Estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable, but it also considers the uncollectible time period for each account. The longer the time passes with a receivable unpaid, the lower the probability that it will get collected. An account that is 90 days overdue is more likely to be unpaid than an account that is 30 days past due. The final point relates to companies with very little exposure to the possibility of bad debts, typically, entities that rarely offer credit to its customers. Assuming that credit is not a significant component of its sales, these sellers can also use the direct write-off method. The companies that qualify for this exemption, however, are typically small and not major participants in the credit market.
A https://www.bookstime.com/ is essential for companies to remove irrecoverable balances from their books. In accounting, doing so is crucial to presenting an accurate picture. At the same time, it decreases the accounts receivable balance on the balance sheet.
Making a bad debt expense journal entry is an adjustment to your accounting for doubtful debt. Whether you use the direct write-off method vs the allowance method, the journal entry is the same. You are putting doubtful debt into an accounts receivable contra account, to document that it is no longer income.
For accurate reporting in accrual accounting, bad debt needs to be written off the books. Holding it in accounts receivable for more than 90 days poses a risk to the accuracy of your accounting.
Cash realizable value in the balance sheet, therefore, remains the same. The term receivablesrefers to amounts due from individuals and companies. Determine the amount of an invoice that a customer is unable to pay.
Bad debt can be reported on the financial statements using the direct write-off method or the allowance method. Bad debt can be reported on financial statements using the direct write-off method or the allowance method. Net receivables are the money owed to a company by its customers minus the money owed that will likely never be paid, often expressed as a percentage. A concentration of credit risk is a threat of nonpayment from a single customer or class of customers that could adversely affect the financial health of the company. If a company has significant concentrations of credit risk, it is required to discuss this risk in the notes to its financial statements. Notes receivable give the holder a stronger legal claim to assets than accounts receivable. After the accounts are arranged by age, the expected bad debt losses are determined by applying percentages, based on past experience, to the totals of each category.
Please check your instagram settings and try again.
Develop by KendyTheme
Copyright © Mover 2019. All rights reserved
